Phase-field fracture(PFF) analysis was not part of my Ph.D. proposal. Still, since there existed a lot of literature on the phase-field method in the domain of fracture, I started learning it to use it further in topology optimization. I got a lot of help from my friend Dr. Tushar K Mandal, who was actively working in the phase-field method at the time. Also, since I was working in FEniCS and there existed an open-source code of PFF in FEniCS by Dr. Hirshikesh and Dr. Emilio Martínez Pañeda, I opted to start learning about phase-field with PFF. One of my colleagues, Meenu Krishnan, also joined me in this effort. All of this led to the development of a generalized and modularized code of PFF in FEniCS with support for parallelization. The code can handle all the three most popular PFF models and supports checkpointing and restart analysis. We also developed time adaptivity and mesh adaptivity algorithms for PFF. This code is one of the significant achievements of my Ph.D.
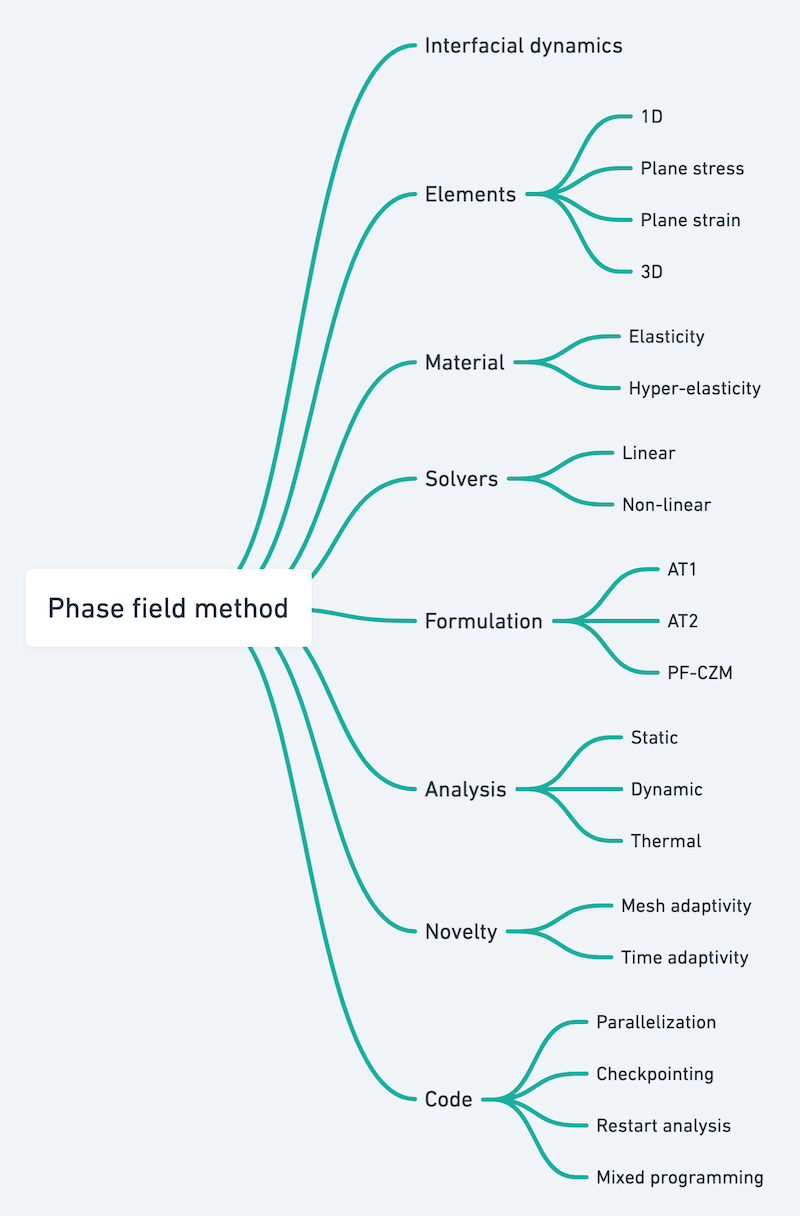
Outcome 1
An auto-adaptive sub-stepping algorithm for phase-field modeling of brittle fracture
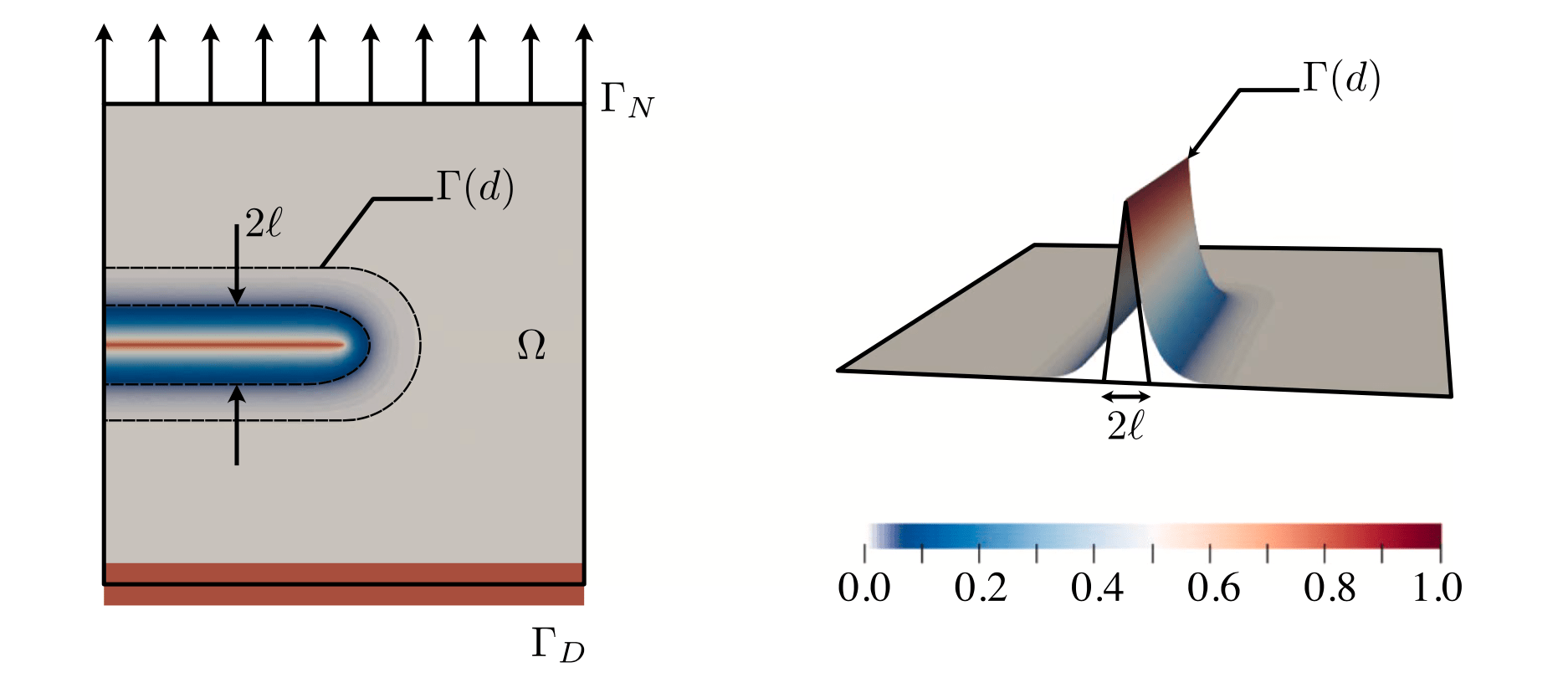
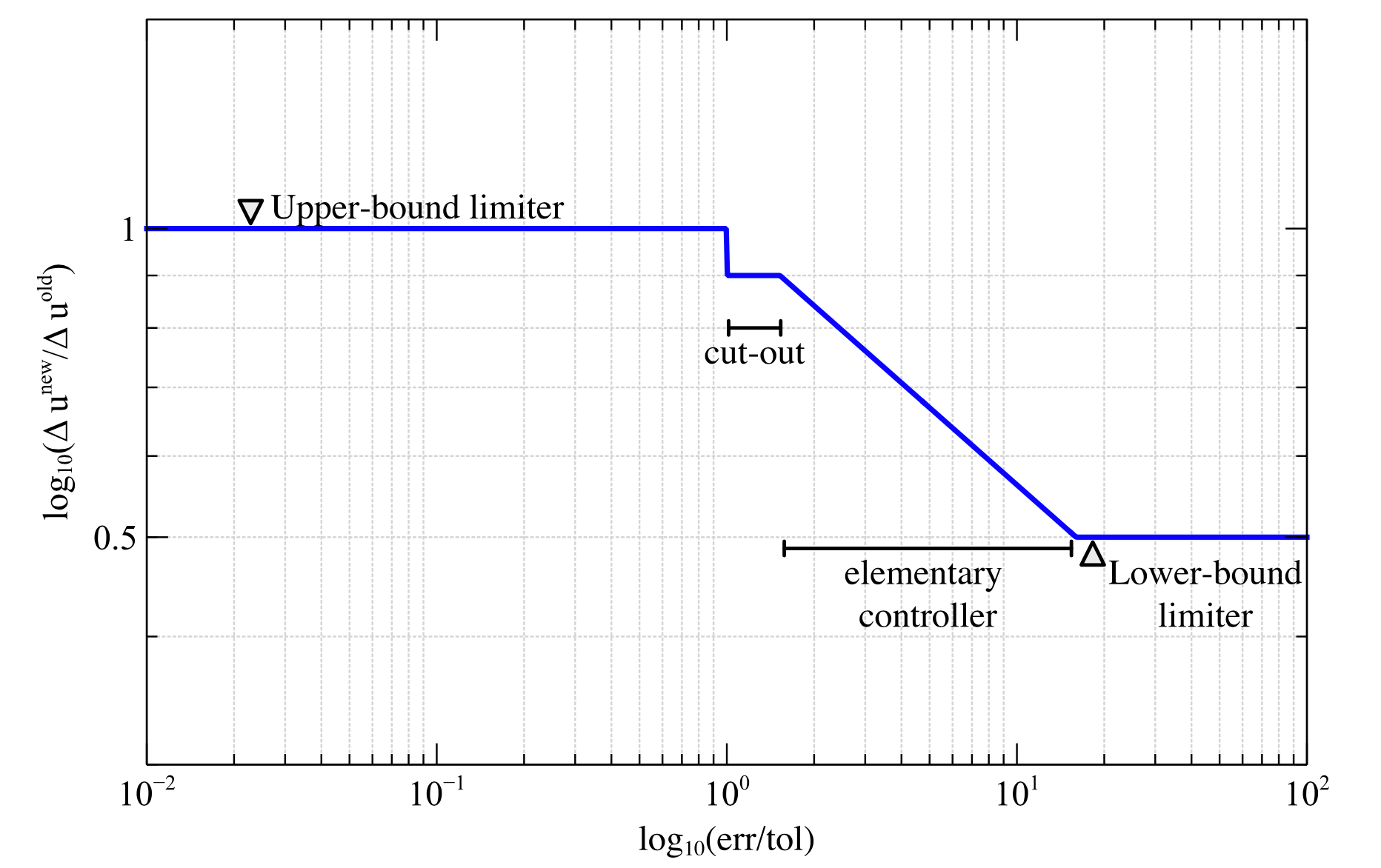
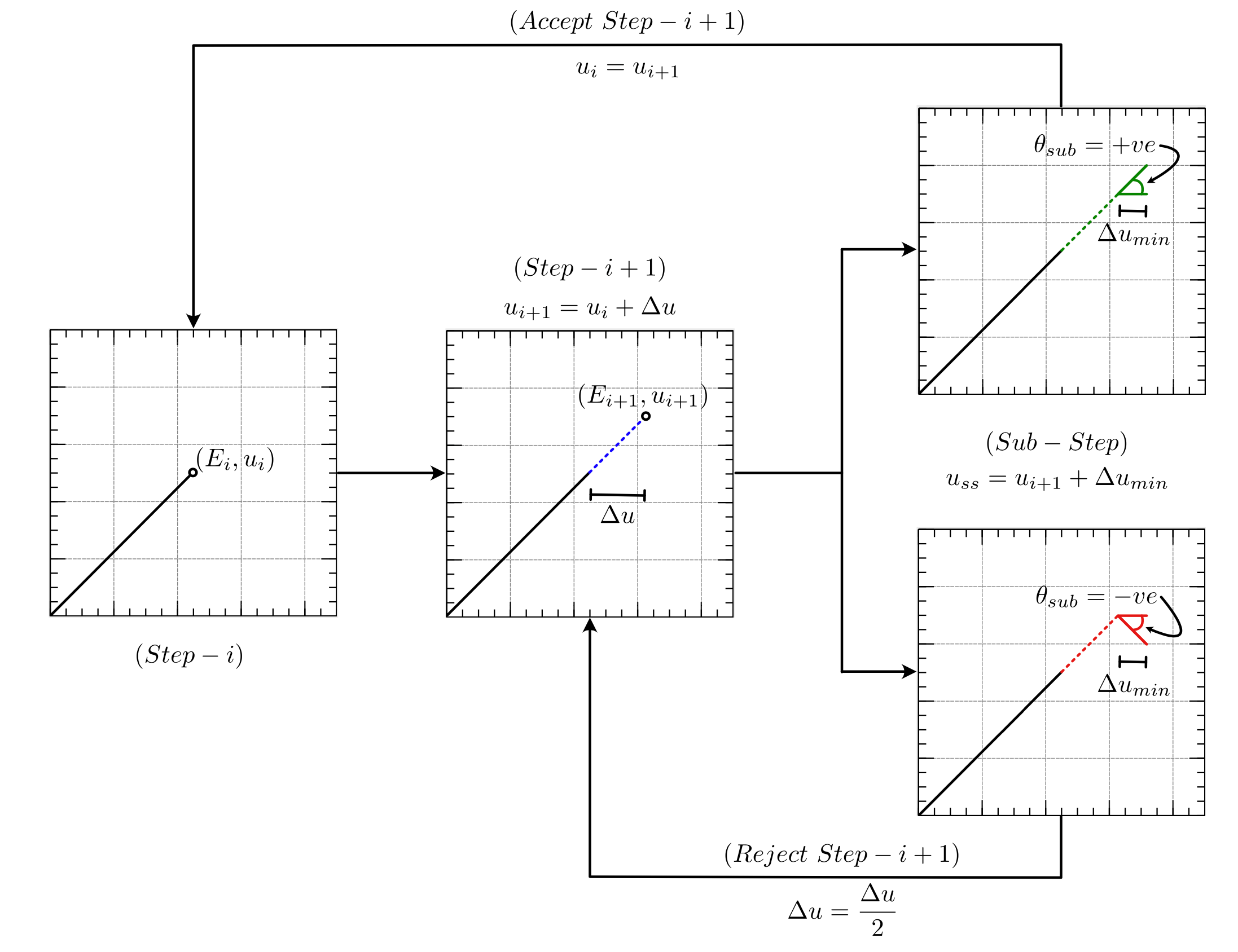
In this work, we propose an auto-adaptive displacement stepping algorithm to auto-adaptively adjust the displacement step size while solving the quasi-static brittle fracture propagation problem with the phase-field method. There were multiple works on adaptive meshing for phase field fracture, but none on adaptive time stepping. Through this project we achieved adaptive time stepping in phase field fracture.
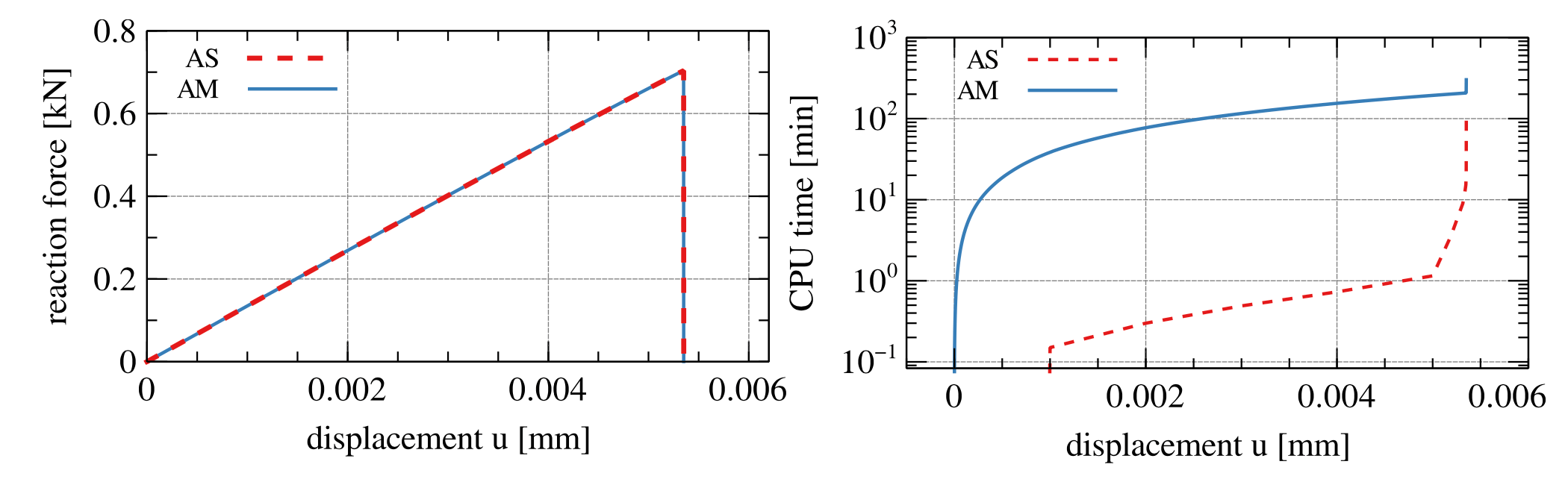
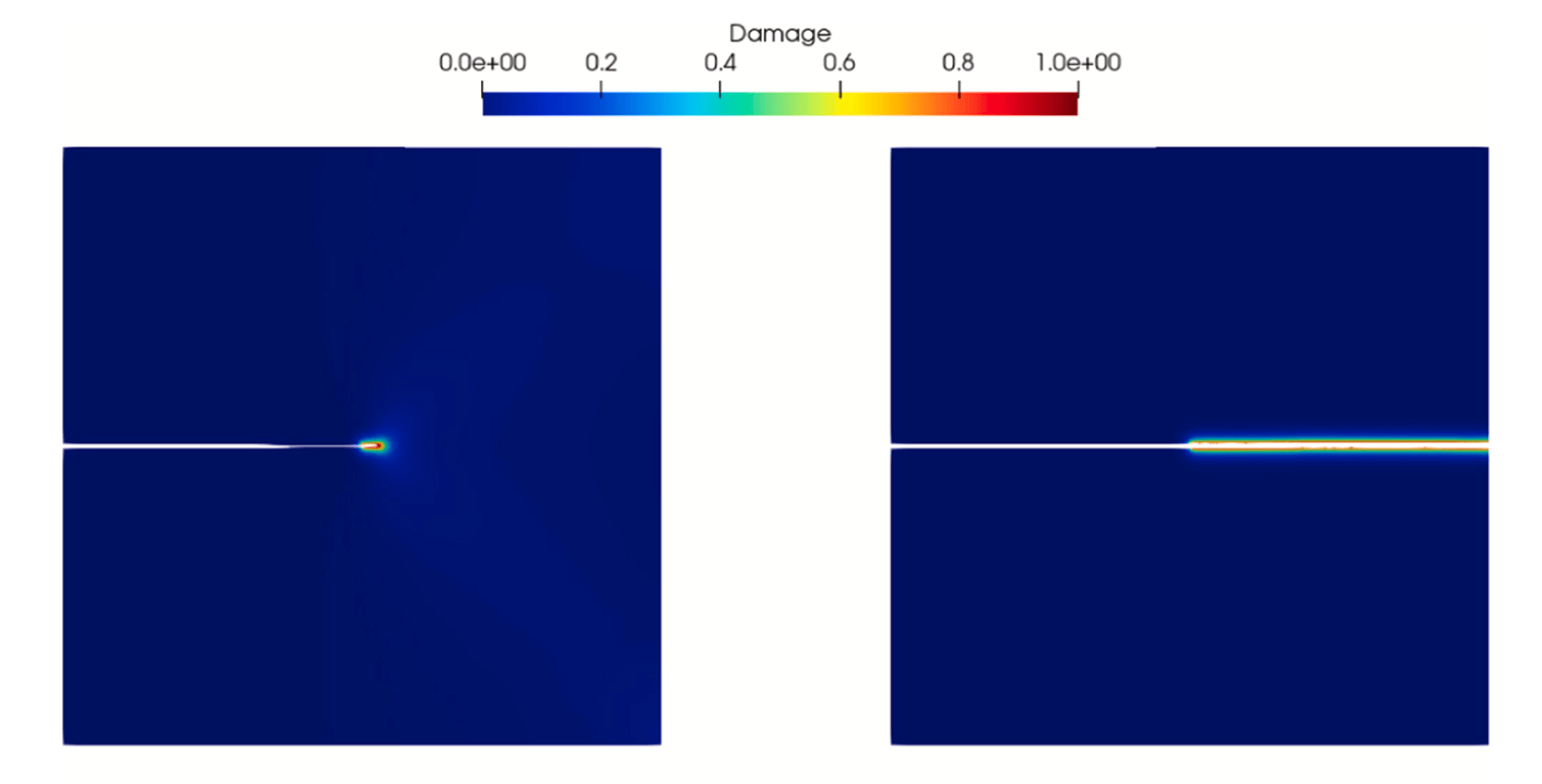
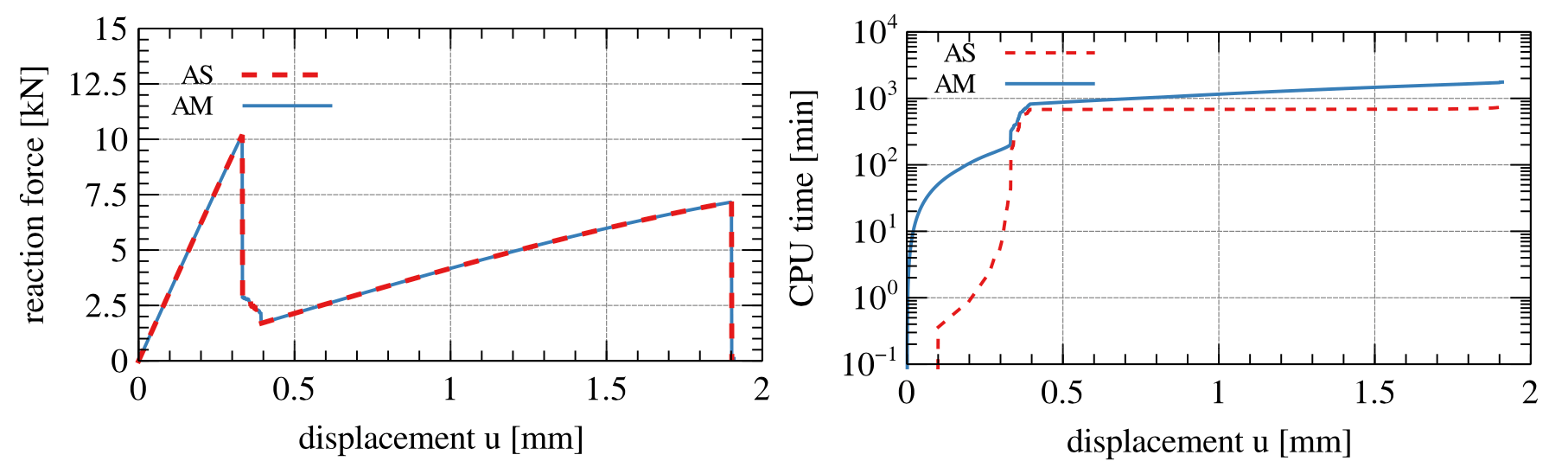
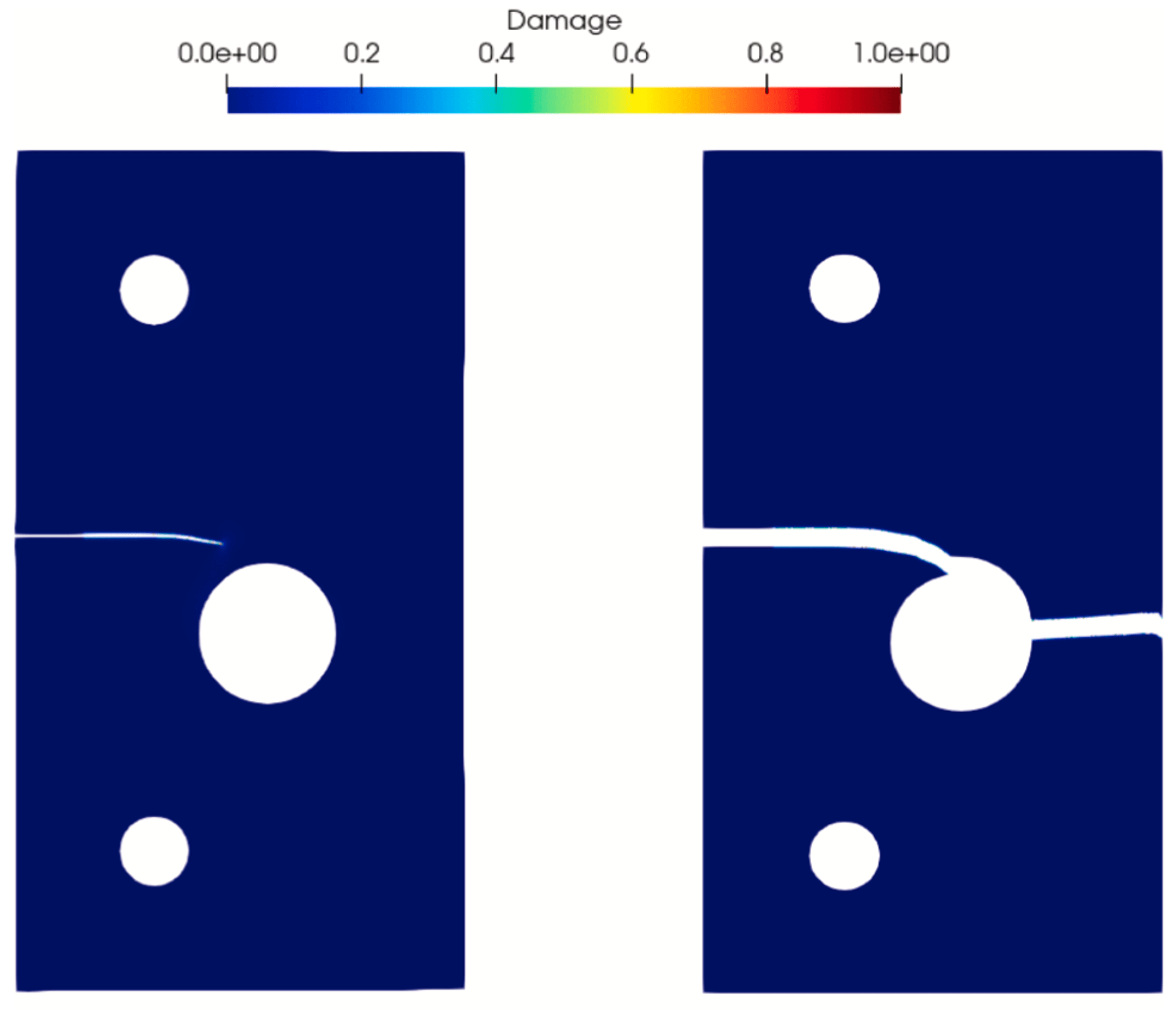
Conclusion
In this work, we proposed an auto-adaptive displacement stepping algorithm with a sub-stepping algorithm to achieve adaptivity in the displacement step for solving the coupled system of non-linear equations arising from the phase field formulation of brittle fracture. We achieved a reduction of 78–90% in the CPU time required to reach the peak reaction force. Also, there is a reduction of 56–78% in the CPU time corresponding to the final solution.
Outcome 2
A length scale insensitive phase field model for brittle fracture of hyperelastic solids